Have you ever wondered how solar panels work? Maybe you’ve seen them on a neighbor’s rooftop and questioned how they generate electricity. Perhaps you even have solar panels on your own roof but don’t know how they provide power to your home. Well you’ve come to the right place. We’re going to take a look at how solar panels create electricity.
The story of how solar electric panels capture sunlight and turn it into electricity is a fascinating one. Ultimately, it’s an inspiring story that proves we are capable of harnessing limitless amounts of clean energy. There is some science involved but we’re going to keep it as simple as possible. And since none of this would be possible without the sun, that’s where we’ll begin.
What is Solar Energy?
Simply put, solar energy is any kind of energy produced by the sun. It also happens to be the most abundant energy resource there is. According to the US Department of Energy, the amount of sunlight that strikes the earth’s surface in ninety minutes is enough to meet the world’s energy needs for a year. That’s pretty impressive!
Solar energy is made up of little packets of energy called photons. Solar cells absorb photons and turn them into moving electrons. This is the key to how solar panels work, so let’s take a closer look at how solar cells get electrons moving.
How a Solar Cell Works
In 1839 Edmond Becquerel exposed an electrolytic cell to light and it generated an electric current. This was the discovery of something called the photovoltaic effect (the generation of an electric current upon exposure to light). It was also the beginning of the solar cell.
Becquerel’s primitive cell eventually led to solar cells made of selenium. The selenium cells then led to silicon solar cells. Silicon is a semiconductor used in many of our modern electronics and it is also what we find in most solar panels today. But how do these modern solar cells turn light into electricity?
The first thing we need to understand is that solar cells consist of two different layers of silicon. These layers are treated so each side has different qualities. One side is deficient in electrons and is called p-type (for positive). The other side has an excess of electrons and is called n-type (for negative). This arrangement creates an electric field that is similar to what you would find in a battery.
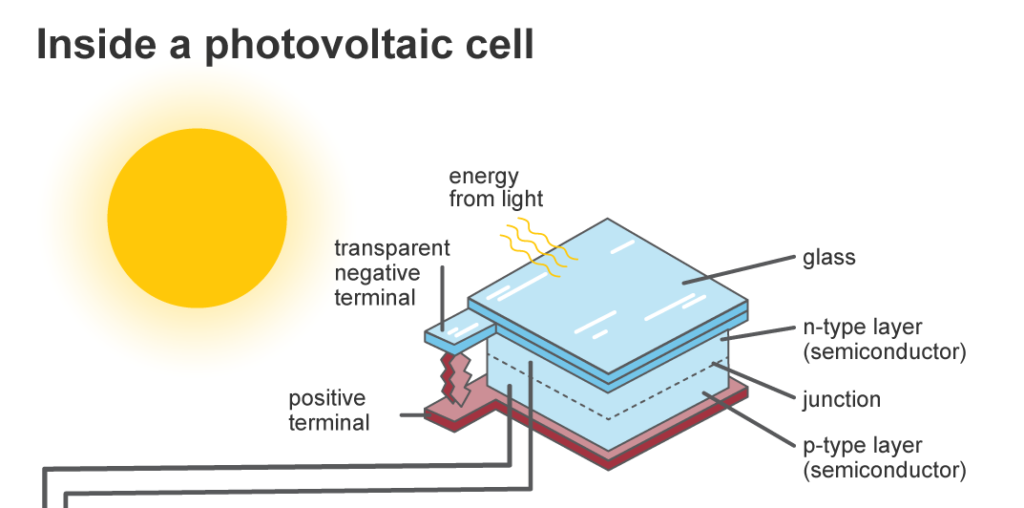
When the photons in sunlight strike the silicon in a solar cell, electrons are knocked loose. At this point, these electrons cross the ‘p-n junction’ between the negative and positive layers of silicon. They are now able to be captured in the form of an electric current. Before this happens, however, electrical conductors must be attached to the positive and negative sides of the solar cell.
In summary, when a solar cell is exposed to sunlight:
- Photons are absorbed by the solar cell
- Electrons in the silicon are knocked loose
- Those loose electrons create an electric current
Check out a visual explanation of how solar cells work in this video from the United States Department of Energy:
How Solar Panels Work
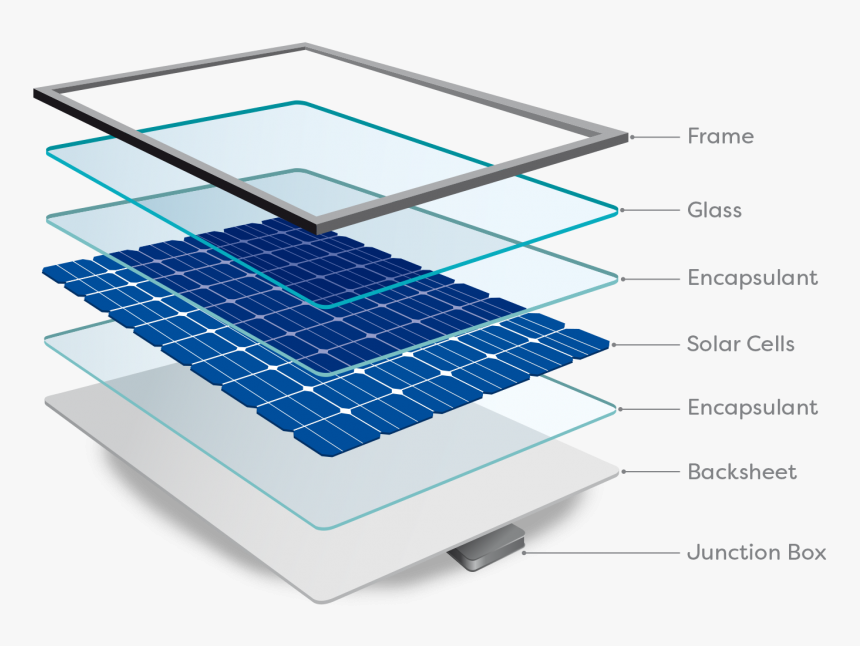
The main components of a typical solar electric panel are:
- Solar Cells
- Solar panels are made up of several individual solar cells. Having many solar cells within the panel allows a significant amount of power to be produced.
- Glass
- A solar panel has a front sheet of tempered glass that protects the solar cells. The glass is usually about 3 mm thick and has an anti-reflective coating that reduces solar energy loss.
- Aluminum Frame
- An aluminum frame covers the edges of the solar panel and provides structural strength. The frame also provides a place to attach the mounting clamps during installation.
- EVA Film
- This ‘ethylene vinyl acetate’ film is a plastic layer that covers both the front and back of the solar cells. This film provides additional protection for the cells and helps to ensure a long panel life.
- Backsheet
- As you might expect, the backsheet covers the back of the solar panel. This polymer or plastic skin acts as a moisture barrier and a final layer of protection.
- Junction Box
- This box is on the rear side of the solar panel. It is the output interface of the solar panel and it allows multiple solar panels to be connected together.
We’ve already seen how a solar cell absorbs the light of the sun and turns it into an electric current. A solar panel brings many of these solar cells together so they can work as a team. The individual solar cells are connected (usually in series) to increase the power and voltage beyond what could be created by a single solar cell.
How a solar panel works can be reduced to these steps:
- Sunlight strikes the solar cells within a solar panel
- Electrons in the silicon are knocked loose
- The electrons form an electric current
- The electric current flows to a conductive wire at the edge of the panel
- The electric current leaves the solar panel
Where does the electric current flow when it leaves the solar panel? To answer that question we have to go beyond how solar panels work and take a look at the bigger picture that includes the entire solar power system.
How Does a Solar Power System Work?
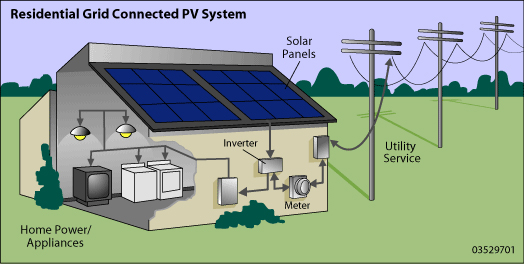
The main components of a solar power system are:
- Solar Panels
- Just as many solar cells are brought together to form a solar panel, many solar panels are brought together to form a ‘solar array’. This is how an entire home can be powered by solar energy.
- Inverter
- Solar panels create direct current (DC) electricity but your home runs on alternating current (AC) electricity. A solar power inverter converts the DC electricity from your solar panel to the AC electricity your home uses.
- Wiring
- Wiring allows multiple solar panels to be connected and it also allows electricity to travel from the panels to your home.
- Utility Meter
- When you have solar panels you will have a ‘bi-directional’ meter. This kind of meter will tell you how much electricity you consumed and how much electricity your solar panels produced.
As we learned previously, when the sun shines on a solar panel it moves electrons and creates an electric current. But where does that current go when it leaves the solar module? It actually travels through a wire to a solar power inverter. The inverter converts the direct current electricity your solar panel produces to the alternating current electricity that your home uses.
After the electricity is converted to alternating current it proceeds to the main electrical panel of your house. It will then be used to power the electrical load of your home.
If there isn’t enough power being produced by the solar panels to cover the home’s electrical load, additional power will be drawn from the electrical grid. If the panels are producing more than the house needs, the excess electricity will be fed back to the grid and your account will be credited. Your bi-directional utility meter will keep track of all these electrical comings and goings.
Will I Still Have an Electric Bill?
Installing solar panels may allow you to eliminate your electric bill completely. This depends on three main factors:
1. The Size of Your Solar Panel System
- If you have a large enough solar power system with enough solar panels you might produce enough power to cover all of your electricity usage.
2. Your Electricity Usage
- If you use a lot of electricity, even a large solar power system might not cover your usage. Your first step should always be reducing your electricity usage wherever possible.
3. The Amount of Sun You Receive
- Needless to say, a solar installation produces a lot more power when it receives a lot of sunshine. In a very sunny area it will be easier to make your electric bill disappear completely.
What About Batteries?
Some solar power systems have batteries to store the power that is produced by the solar panels. Your solar panels will produce electricity in the same way whether you have batteries in your system or not. Things work a little differently after the electricity leaves the solar panel, however.
When a solar system has batteries, electricity doesn’t travel directly from the solar panel to the inverter. The electricity first travels to a charge controller and then to the battery bank. The battery bank stores the excess electricity generated by your solar panels.
Learn more about batteries on our solar batteries page.
Conclusion
Hopefully this information provides you with a better understanding of how solar panels work. Maybe it will even inspire you to go solar and put the power of the sun to work in your home! If you’re interested in learning more about how different technologies harness solar energy, check out our page on how solar power works.
